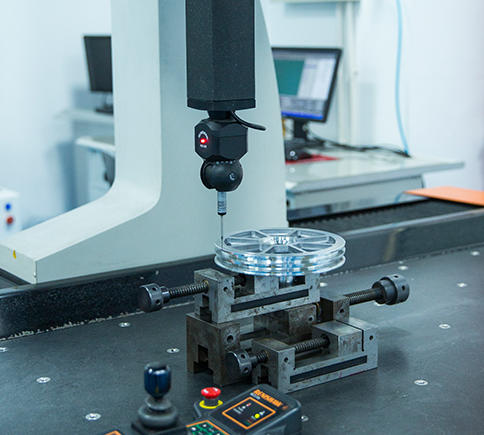
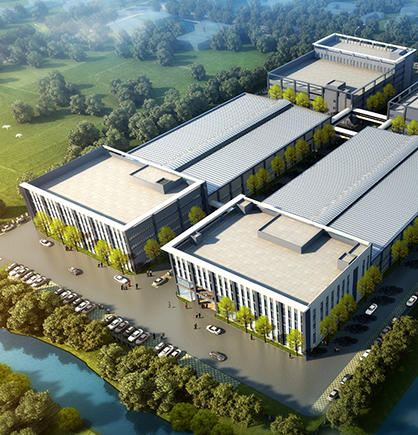
Who
we are
Who
we are












Versatility: Pneumatic presses are highly versatile and can be used for a wide range of applications, such as pressing, punching, stamping, forming, riveting, and more. They can handle different materials, including metal, plastic, wood, and composites.
Fast and Efficient: Pneumatic presses provide rapid and consistent press cycles, allowing for high productivity and efficient operations. They can generate high forces quickly, reducing production time and increasing output rates.
Precise Control: Pneumatic presses offer excellent control over the applied force, stroke length, and press speed. The compressed air can be regulated to achieve precise pressure and position control, ensuring accurate and repeatable results. This makes them suitable for applications requiring fine-tuned force application or delicate materials.
Safety: Pneumatic presses are generally safer to operate than hydraulic or mechanical presses. They have built-in safety features, such as overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and two-hand control systems. They also do not pose the risk of hydraulic fluid leaks, reducing the potential for environmental contamination.
Compact and Lightweight: Pneumatic presses are usually compact and lightweight compared to their hydraulic counterparts. They take up less space and can be easily integrated into existing production lines or workspaces. Their portability allows for flexible placement and repositioning as needed.
Cost-Effective: Pneumatic presses tend to be more cost-effective compared to hydraulic or mechanical presses, both in terms of initial investment and maintenance. They have fewer complex components, require less maintenance, and have lower operating costs, as they do not require hydraulic fluids or extensive power systems.
Pneumatic presses can be used for a variety of applications, including precision and high-force tasks, depending on their design and specifications. However, their suitability for these applications may vary compared to other types of presses, such as hydraulic or mechanical presses. Let's explore some considerations regarding the use of pneumatic presses for precision and high-force applications:
Precision: Pneumatic presses can offer a certain level of precision, but they may not be as precise as some other types of presses. This is because pneumatic systems typically rely on air pressure, which can have slight variations and may result in a small amount of play or movement in the press mechanism. If precise control is crucial, such as in applications requiring very tight tolerances, other press types like hydraulic or servo-driven presses might be more suitable.
Force: Pneumatic presses can generate significant force, especially when high-pressure air is used. They can achieve substantial tonnage and exert considerable power during operation. However, their force capabilities may be limited compared to hydraulic or mechanical presses, which can handle extremely high forces. If your application requires exceptionally high force levels, you might want to explore other press options.
Speed: Pneumatic presses are generally known for their high-speed operation. They can rapidly cycle and provide fast stroke speeds, which can be advantageous in certain applications. However, the trade-off for speed is often reduced force capabilities or precision. So, it's important to consider the specific requirements of your application to determine if the speed of a pneumatic press aligns with your needs.